Electrical Safety Standards and Basic Testing
Electrical safety standards
To help verify the functionality and safety of medical devices, electrical safety standards have been established in the United States, European countries, and other parts of the world. The standards differ in criteria, measurements, and protocol. The International Organization for Standardization (ISO) and the International Electro-technical Commission (IEC) organizations based in Europe provide standards worldwide in partnership with the World Trade Organization. These include standards for electro-medical equipment. There are general and specific standards for medical device electrical safety. IEC60601 AAMI/NFPA 99 The primary standard for medical devices is IEC 60601. General requirements for protection against electric shock hazards are covered in IEC 60601.1, Section 3.
In this standard, each instrument has a class:
- Class I—Live part covered by basic insulation and protective earth
- Class II—Live part covered by double or reinforced insulation
- Class IP—Internal power supply
Each patient applied part or patient lead has a type:
- Type B—Patient applied part earthed
- Type BF—Patient applied part floating (surface conductor)
- Type CF—Patient applied part floating for use in direct contact with the heart
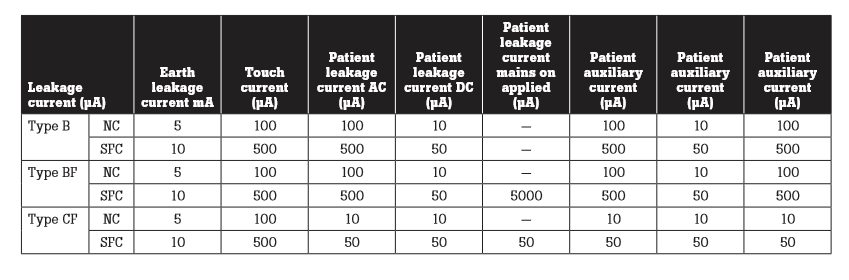
Leakage measurement limits have been developed for equipment types and measurements. They include:
- NC—normal conditions
- SFC—single fault conditions
The terminology used in IEC 60601.1 3rd Edition includes:
- Protective earth resistance
- Earth leakage current
- Touch current (formerly enclosure leakage current)
- Patient leakage current
- Patient auxiliary current
- Mains on applied part (MAP)
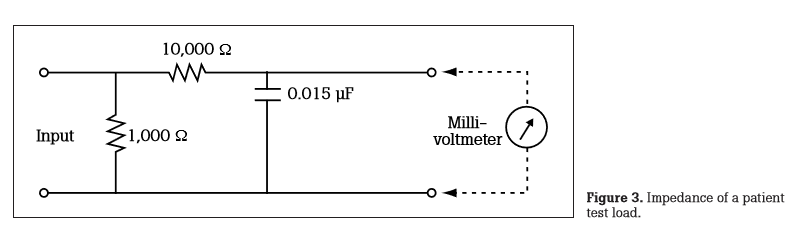
The figure above represents the impendence of a patient test load. Leakage current measuring devices use this impedance circuit for measurements.
Additional important points regarding IEC 60601.1 include:
- The use of up to 25 amperes ac for protective earth testing (this is a type-test and generally suitable for manufacturers)
- Leakage current is measured at 100 percent of mains voltage
- Performance of dielectric strength/insulation testing is measured at 110 percent of mains voltage.
A new IEC standard, IEC 62353, is used for medical device testing in hospitals. IEC 62353 was developed because IEC 60601.1 is a type-testing standard with no risk management criteria and is impractical for testing in the hospital environment.
IEC 62353 tests are performed on equipment prior to use on patients, during schedule periodic testing, and after repair. Thus, this standard is for field (hospital) testing and does not address equipment design. In Annex E of the document, the manufacturer is requested to provide information on testing interval and procedure based on risk, typical usage, and device history. The minimum testing requirement for life support and other critical equipment is every 24 months.
In the United States, there are several primary and secondary organizations setting standards:
- National Fire Protection Association (NFPA): NFPA 99 Standard for Health Care Facilities is the primary standard addressing electrical safety testing required in health care institutions. Other publications include NFPA 70, National Electrical Code, and NFPA 70E, Electrical Safety in the Workplace.
- Association for the Advancement of Medical Instrumentation (AAMI): ANSI/AAMI ES1 Safe Current Limits for Electro-medical Apparatus is another commonly-accepted standard.
- Underwriters Laboratories (UL): UL544, Medical Equipment requirements is a standard for manufacturers, not hospitals. These standards may be referenced by accreditation, code or regulatory organizations such as the Joint Commission, Occupational Health and Safety Administration or other organizations monitoring health care institutions in the United States.
- Canadian Standards Association (CSA): CAN/CSA C22.2 NO. 60601-1-08 Medical Electrical Equipment Part 1: General Requirements for Basic Safety and Essential Performance (Adopted IEC 60601-1:2005, third edition, 2005-12)
Global harmonization of standards has led to the development of worldwide standards. Equipment in the regions listed below must be certified to the IEC60601-1 standard or the device cannot be sold in that country.
- USA uses UL2601-1 or ANSI/AAMI ES601
- Europe uses EN60601-1
- Canada uses CAN/CSA-C22.2 No. 601.1-M90

Electrical safety testing
Testing requirements and sequence according to IEC 62353 Annex C are shown below. Only measurement equipment that meets IEC 61010-1 should be used. The sequence outlined in the figure below should be followed. For example, protective earth resistance should be measured prior to leakage current measurements
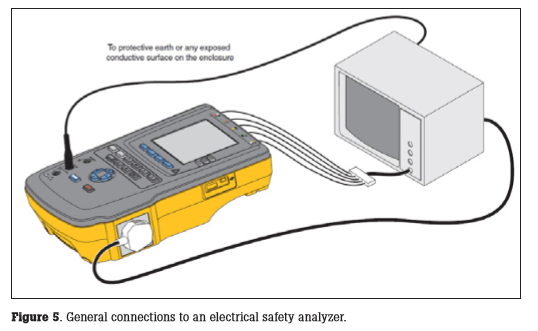
General connections to an electrical safety analyzer (ESA) are shown in Figure 5. Consult the operational manual for specifics for your electrical safety analyzer. Documentation requirements for IEC 62353 include:
- Identification of the testing group (hospital department, independent service organization, manufacturer)
- Names of the person(s), who performed the testing and evaluation(s)
- Identification of the equipment/system (e.g. type, serial number, inventory number) and the accessories tested
- Tests and measurements
- Date, type, and outcome/results of:
- Visual inspections
- Measurements (measured values, measuring method, measuring equipment)
- Functional testing
- Concluding evaluation
- Date and signature of the individual who performed the evaluation
Computerized record-keeping systems are greatly preferred for data storage, search, review, and analysis. Note the device fields must be standardized.
The ESA609 integrates all functions needed to test medical devices when patient lead testing is not required, including:

- Line (mains) voltage
- Ground Wire (or protective earth) resistance
- Equipment current
- Ground wire (earth) leakage
- Chassis (enclosure) leakage
- Direct equipment leakage
- Point to point leakage and resistance
Versatile to global electrical safety standards of choice, the ESA609 tests to ANSI/AAMI ES1, NFPA-99, and parts of IEC62353 and IEC60601-1.
To learn more about the ESA609 Electrical Safety Analyzer visit www.flukebiomedical.com/ESA609.
