Training
The Advantage Training site provides free and instant access to both basic and advanced medical device quality assurance training courses. With Advantage Training, you can stay up-to-date on all the latest techniques and tools from Fluke Biomedical and RaySafe.
Advantage Training Program - On-demand training
The Advantage Training site provides free and instant access to both basic and advanced medical device quality assurance training courses. With Advantage Training, you can stay up-to-date on all the latest techniques and tools from Fluke Biomedical. Track your training and receive certificates for training completion.
Sign up today!
To register for Advantage Training, click the "Get Training Now" button to the right. Follow the step-by-step instructions to complete the registration.
For more details follow this how-to register guide:
How-to Register Guide
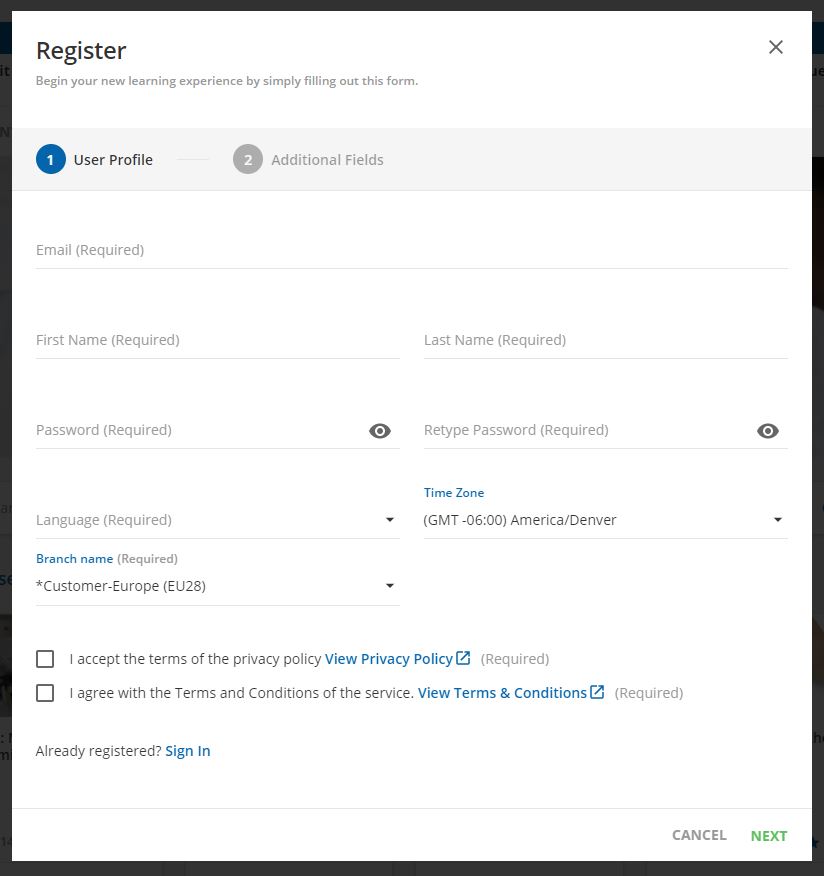
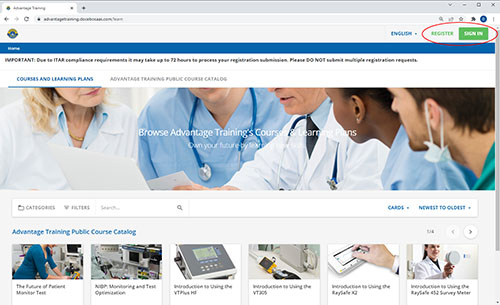
Step 1:
Click the "Register" button in the upper right corner
Step 2:
Fill out registration and click "next"
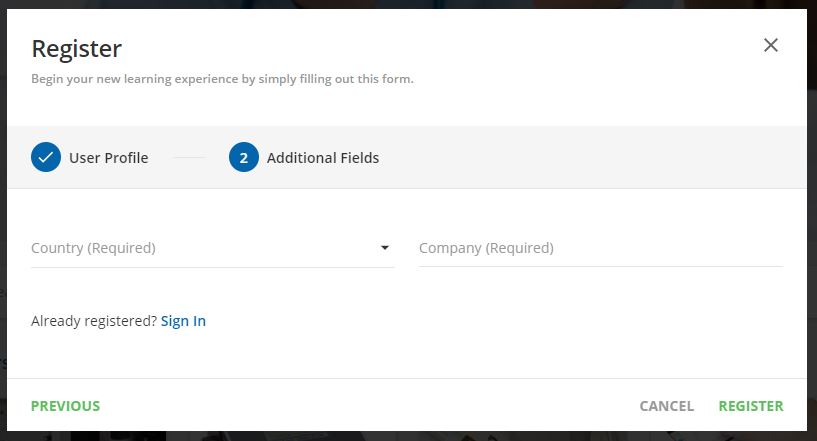
Step 3:
Complete and click "register"
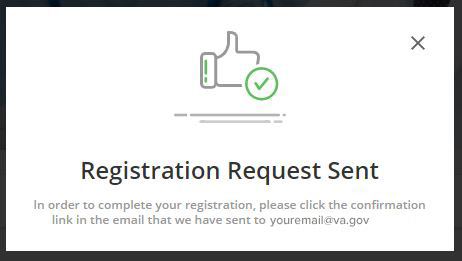
Step 4:
Confirmation email sent to your email to confirm
Step 5:
Congratulations - your account has been created.
If you already have an Advantage Training account with your email. Use the links below to specific training categories.

Defibrillator Testing
Register for basic defibrillator analyzer training.
Defibrillators include many more patient parameters, modes of operation and innovative designs than ever before. Among these are temporary transcutaneous pacemakers, AED-like automatic assessment of arrhythmias, and algorithms and circuitry that ensure defibrillation-therapy-energy delivery based on the settings. Older test instruments may not be able to test these newer design capabilities.
- Why 50 ohm test loads are no longer enough
- Defibrillator and AED best practices
- Why you need to test AEDs
- Charge time testing? When, how, what energy?
- Test Automation Software time savers
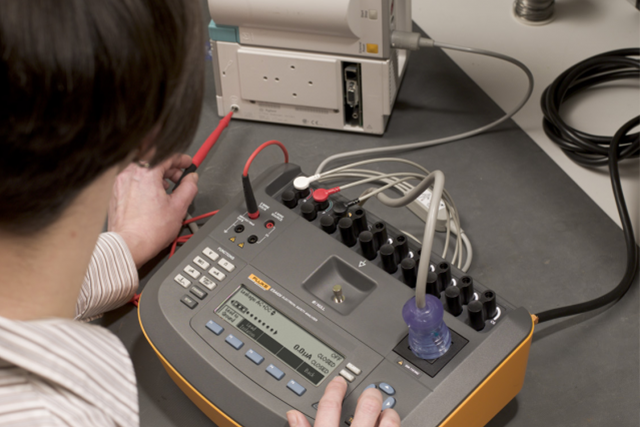

Electrical Safety Testing
Start your biomedical engineering training today.
Electrical safety testing was the first mandate of biomedical engineering, and why biomedical engineering was brought into the hospital as a functional area in the 1970’s. Today there are many electrical safety standards, most of which have been harmonized with the IEC standards found under IEC 60601. The basis standards (IEC 60601-1 and IEC 62353) are constantly under review and revision. Not only is it hard to keep up, it is also not easy to understand how to apply testing methodologies, or testing limits.
- Similarities and differences between tests, terminology, and standards
- How to easily perform basic tests; simple solutions for in-depth testing
- How automatic test instrument configuration and measurement data collection make testing more efficient
- How visually-guided testing with predetermined test limits standardizes work, reduces human error
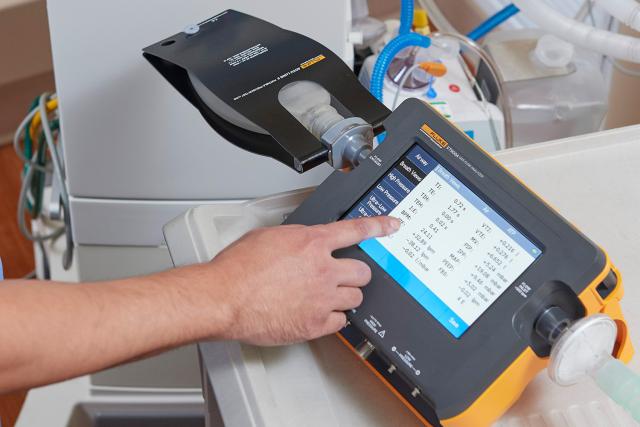

Gas Flow/Ventilator Testing
Medical device technician training for gas flow testing is now available.
Medical gas flow and pressure are produced by many more kinds of medical devices besides ventilators and anesthesia systems. While ventilators and anesthesia systems have specific requirements for complete quality assurance testing, the basics of flow, pressure, and time are fundamental. Endoscopic insufflators, tracheal and wound suctioning devices, side-stream-sampling gas concentration monitors, flow meters, vacuum pressure gauges, and more are in the inventory of every hospital, clinic, and doctor’s office.
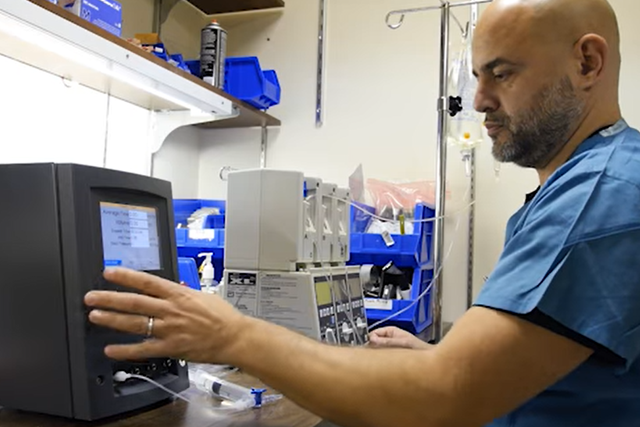

Infusion Pump Testing
Biomedical equipment maintenance training focused on infusion pump testing.
While small hospitals and clinics may include a manageable quantity of infusion pumps, including enteral feeding pumps, syringe pumps, infusion controllers, larger medical facilities often include as high a quantity as 3 infusion devices per bed. This number can reach seemingly un-manageable quantities compared to the biomedical engineering department staff available to perform medical device quality assurance testing. Recently the high incidence of failure across all makes and models of infusion devices has caused the US FDA to focus its attention on reducing the un-managed risk to the patient posed by these failures. Batch-testing may provide a more economically acceptable method for completing tests.
What can I learn here?
- Why only electronic burette technology can test multiple pumps and multiple channels efficiently and cost-effectively
- How easy it is to perform basic tests accurately and to include in a batch-testing method
- How automatic test instrument configuration and measurement data collection make testing more efficient
- How visually-guided testing with predetermined test limits standardizes work, reduces human error
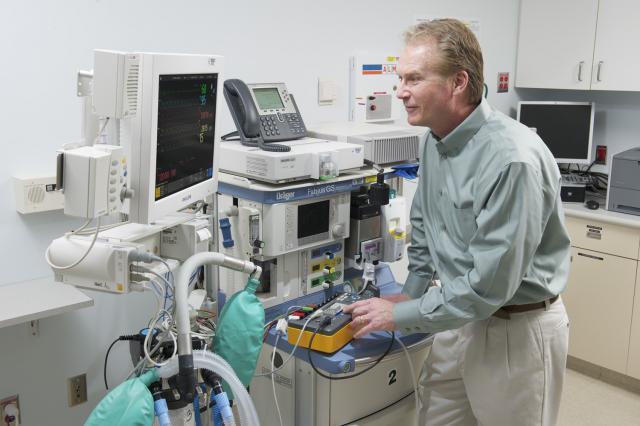

Patient Monitor Testing
Access self-paced module for the patient monitor testing chapter in the new medical device quality assurance curriculum.
Patient monitors were among the first electronic technologies to be brought into the hospital. Though patient monitor designs have dramatically improved reliability, the frequent failure of patient-connected sensors still makes it important to perform quality assurance testing. Innovative technologies that have improved NIBP-measurements during patient movement, and brought diagnosis formerly available only after clinical laboratory analysis of blood samples cannot be tested with older test instruments. Patient monitor testing is far from routine. The patient monitor testing courses introduce new concepts for patient monitor quality assurance (performance and safety testing, documenting for regulatory compliance, productivity improvement, and using test instruments effectively).
What can I learn here?
- Why NIBP accuracy can only be determined using static pressure comparisons
- What NIBP dynamic simulations actually tell us about performance repeatability
- Why clinical condition-based simultaneous, in-parallel, correlated simulations make testing fast while still complying with the manufacturer’s specified inspection procedure
- How visually-guided test procedures speed scheduled inspections and PM
- Troubleshooting versus routine performance

Oscilloscope Testing
What you as a biomedical equipment technician need to know.
Everywhere that diagnostic imaging or endoscopic surgeries are performed in the hospital, or clinic, and everywhere video cameras are used to see the patient from a distance (neurological ICUs, isolation rooms, etc.) there is the potential for time-chain problems requiring an oscilloscope to troubleshoot. Balancing 3-phase power coming into the power supplies of diagnostic imaging systems, renal dialysis systems, a multiple channel oscilloscope and digital multi-meter finds labor-saving use. Troubleshooting power line transients (previously requiring a line transient recorder) may be another use for a recording-oscilloscope to capture not only the numerical fact and instance of the transient, but how it looks on the voltage waveform or current waveform.
What can I learn here?
- Introduction to 190M: form, function, and feature set
- Learn situations where the 190M is the best troubleshooting tool to use
- How easy it is to determine root cause
- Why adding the 190M improves assessment of certain categories of medical devices (e.g. Defibrillators, ESU's, etc.)

X-Ray Beam & Dose Quality Testing
Get radiation safety training and understand the real value of quality assurance.
Diagnostic X-ray system quality assurance testing is done by radiographic engineers (who may report to biomedical engineering, radiology, health physics or medical physics department in hospitals or independent contractor companies). Safety and effectiveness for clinical use is determined by medical health physicists who may also serve as radiation safety officers. While physicists are generally well trained on testing tools needed for dose assessment and image quality, they leave the assurance of performance and safety of the X-ray systems to radiographic engineers. Both these groups are ultimately trying to reduce risk to the patient from detrimental, accumulative effects of exposure to ionizing radiation. Biomedical engineering departments are well advised to make sure that staffing, training, test instruments and other testing tools (including phantoms) are available before jumping into full maintenance responsibility for X-ray systems. An easier entry point is first-call troubleshooting, and so both first-call and full maintenance responsibility are included in the scope of training.
What can I learn here?
- Achieve real value in first-call decisions
- Manage risk, minimize dose, and maximize up-time
- Why ion chambers are the right tool for AEC systems
- How test automation and electroinc test results help predict tube replacement and keep cost under control
- How to use X-ray testing tools effectively
- When an oscilloscope is the right choice for testing